Technology Can Help Solve Caribbean Healthcare Challenges
The Caribbean faces persistent healthcare challenges: limited specialist availability, geographic barriers to accessing care in rural areas, chronic disease prevalence, and strained public health systems. Mobile health technology — often called mHealth — has the potential to address these challenges by bringing healthcare information, monitoring, and even consultations directly to patients through their smartphones.
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated telemedicine adoption across the Caribbean, demonstrating that both patients and healthcare providers are willing to embrace digital health tools when the need is clear. This shift in attitudes, combined with high smartphone penetration rates, creates a favorable environment for health tech app development in the region.
Telemedicine Applications
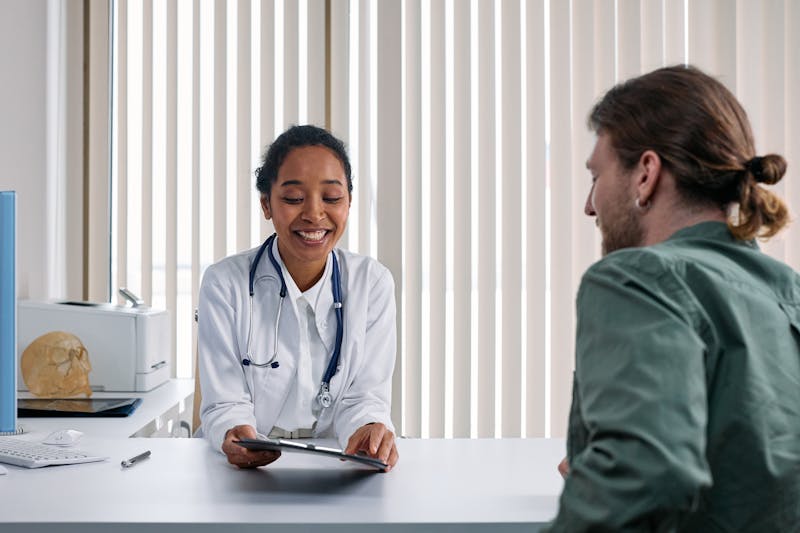
Telemedicine apps connect patients with healthcare providers via video, audio, or text consultations. For Caribbean patients who would otherwise need to travel hours to see a specialist, or who face long wait times at public clinics, telemedicine provides meaningful access improvements. Key features include appointment scheduling, secure video consultation, prescription management, and medical record access. Integration with local pharmacies for prescription fulfillment and local payment processors for consultation fees are Caribbean-specific requirements that generic telemedicine platforms often lack.
Chronic Disease Management
Non-communicable diseases — diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular disease — are the leading cause of death in the Caribbean. Apps that help patients manage these chronic conditions can have a measurable impact on health outcomes. A diabetes management app might track blood glucose readings, medication adherence, dietary intake, and exercise, providing insights and alerts that help patients and their doctors make better decisions. The key is making these apps simple enough that they become part of the patient's daily routine rather than an additional burden.
Health Data Privacy and Compliance
Health data is among the most sensitive categories of personal information. Caribbean health tech developers must implement rigorous data protection measures. Encrypt all health data in transit and at rest. Implement strict access controls so that health information is accessible only to authorized users. Provide clear, understandable privacy policies that explain what data is collected, how it is used, and who has access. While Jamaica's Data Protection Act provides a general framework, health tech developers should also consider international standards like HIPAA as a benchmark for best practices, particularly if serving diaspora users in the US.
Designing for Healthcare Accessibility
Health tech apps must be accessible to users across a wide range of ages, technical literacy levels, and physical abilities. Many chronic disease patients are older adults who may be less comfortable with smartphone technology. Use large text sizes, high contrast colors, simple navigation, and clear instructions. Minimize the number of steps required to complete common tasks like logging a blood pressure reading. Provide audio instructions or video tutorials for first-time users. Consider supporting multiple languages if serving diverse Caribbean populations.
Partnering with Healthcare Providers
The most successful health tech apps are developed in close collaboration with healthcare providers who understand patient needs and clinical workflows. Engage doctors, nurses, pharmacists, and public health officials early in your development process. Their input ensures that your app solves real clinical problems rather than technology problems looking for a healthcare application. Partnerships with healthcare institutions also provide credibility, user acquisition channels, and the clinical validation necessary for adoption by both providers and patients.